Worksheet that describes each phase of the cell cycle interphase Biology Diagrams
Worksheet that describes each phase of the cell cycle interphase Biology Diagrams The cell cycle is a 4-stage process consisting of Gap 1 (G1), synthesis (S), Gap 2 (G2), and mitosis (M), which a cell undergoes as it grows and divides. After completing the cycle it either starts the process again from G1 or exits through G0. From G0, the cell can undergo terminal differentiation.

Phases of Cell Cycle. Cell cycle or cell division refers to the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its maturity and subsequent division. These events include duplication of its genome and synthesis of the cell organelles followed by division of the cytoplasm. Human cells exhibit typical eukaryotic cell cycle and take around
Definition And Phases of Cell Cycle Biology Diagrams
The cell cycle consists of distinct phases that guide cellular activities from one stage to the next. Each phase has specific functions and checkpoints to maintain genomic integrity and prevent errors. It is a dynamic period where the cell assesses its environment and internal conditions to ensure readiness for the next steps. Regulation of Cell cycle, the ordered sequence of events that occur in a cell in preparation for cell division. The cell cycle is a four-stage process in which the cell increases in size, copies its DNA, prepares to divide, and divides. For a stimulatory signal to reach the nucleus and "turn on" cell division, four main steps must occur. First, a
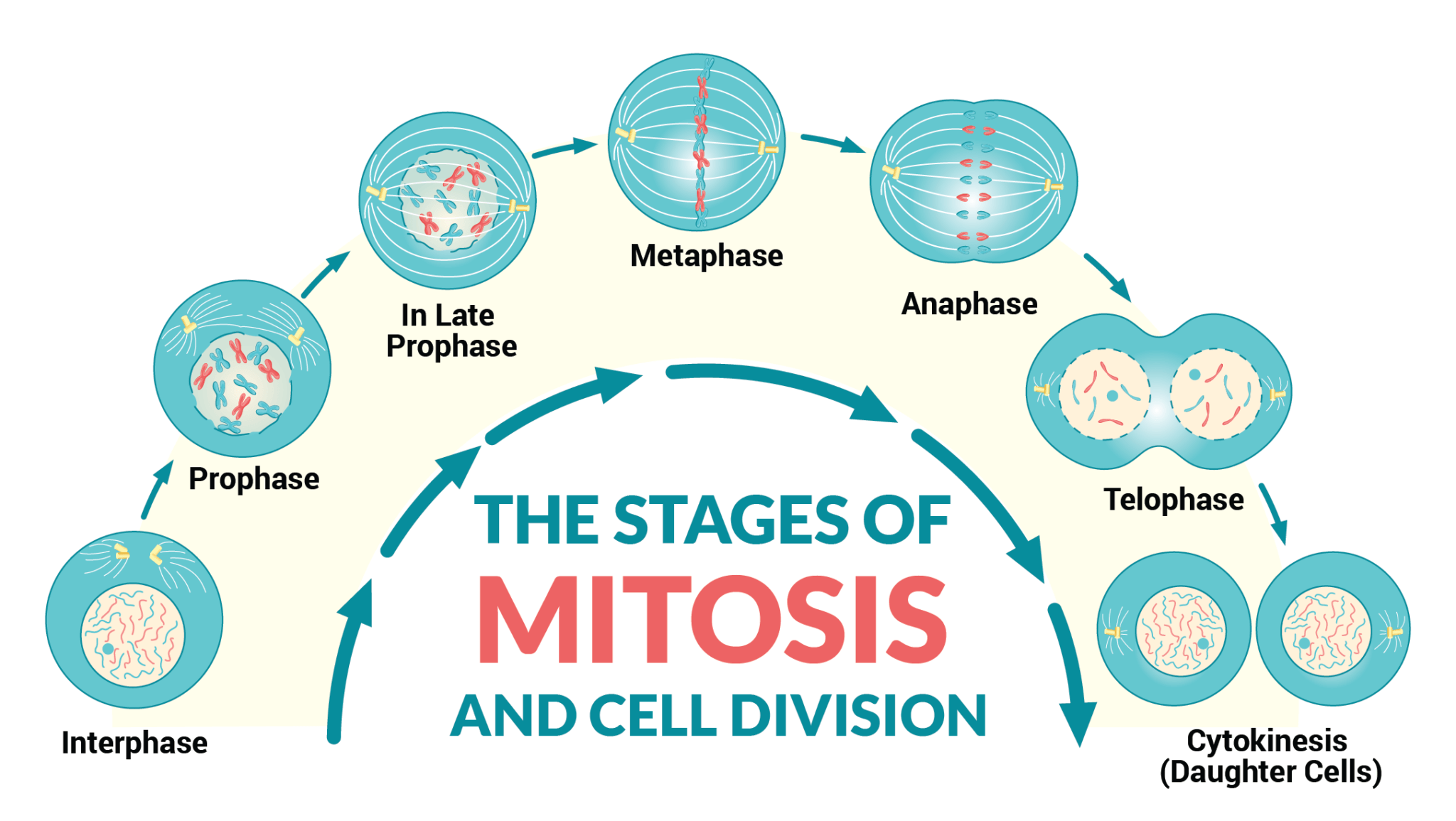
The overall process and steps of the cell cycle might differ in eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms as a result of the differences in their cell complexity. Three main cycles are involved in the cell cycle; chromosome cycle, cytoplasmic cycle, and centrosome cycle. The chromosome cycle involves DNA synthesis that alternates with mitosis.
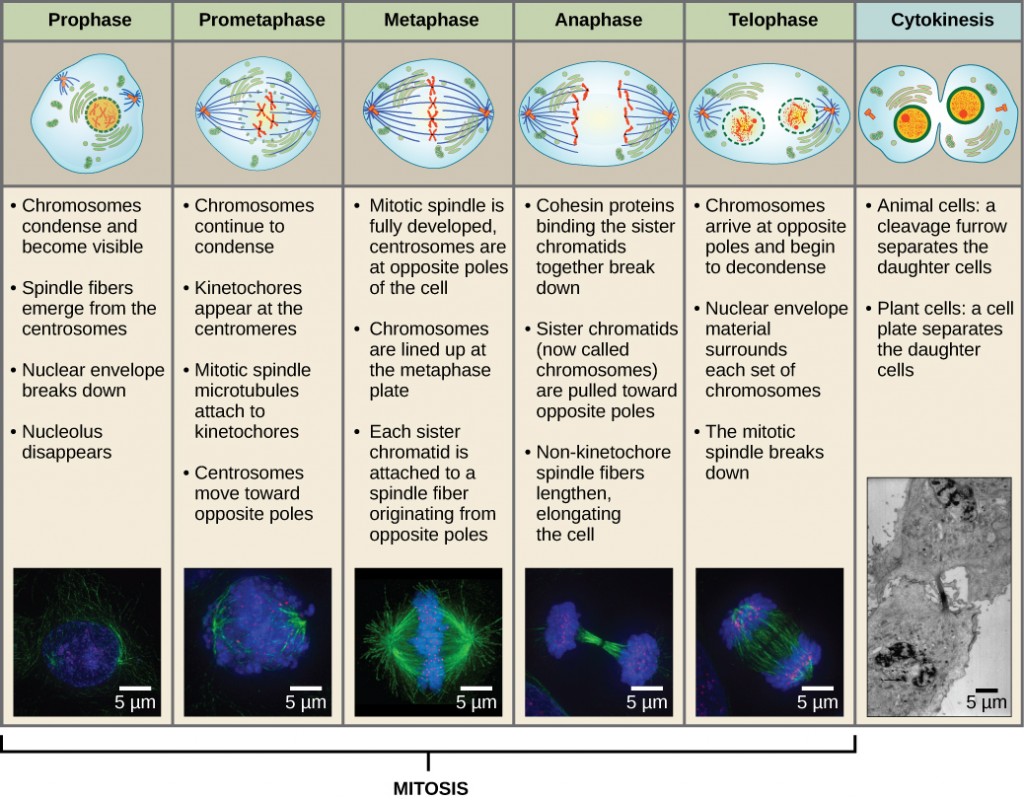
Cell Cycle: Definition, Phases, Regulation, Checkpoints Biology Diagrams
Learn about the cell cycle, the cycle of stages that cells pass through to divide and produce new cells. The cell cycle consists of two main parts: mitosis and interphase, which are further divided into sub-phases such as G 1, S, and G 2. Cells divide into new (daughter) cells through a series of events that take place in steps. The products formed in each round replicate the process in the next round. A cell cycle is thus a sequence of events that a cell goes through as it grows and divides to produce new cells. Therefore, it can be called the life cycle of a cell.
